📚
Course Summary
For Stats 1 summary click here.
For English 1 summary click here.
For Qualifier exam click here.
Week 1 to 4 (Qualifier)
Week 1: Relations and Venn Diagrams
In the first week, we focused on understanding different types of relations: reflexive, symmetric, transitive, and equivalence relations. We also explored the use of Venn diagrams to solve problems involving sets.
Important Concepts:
- Reflexive Relation: A relation \( R \) on a set \( A \) is reflexive if \( \forall a \in A, (a, a) \in R \).
- Symmetric Relation: A relation \( R \) on a set \( A \) is symmetric if \( \forall a, b \in A, (a, b) \in R \implies (b, a) \in R \).
- Transitive Relation: A relation \( R \) on a set \( A \) is transitive if \( \forall a, b, c \in A, (a, b) \in R \land (b, c) \in R \implies (a, c) \in R \).
- Equivalence Relation: A relation that is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
Venn Diagram Formula:
$$|A \cup B \cup C| = |A| + |B| + |C| - |A \cap B|$$
$$- |A \cap C| - |B \cap C| + |A \cap B \cap C|$$
Example:
Suppose we have three groups of people: those who like football, hockey, and cricket. Let:- \( |A| = 30 \) (football)
- \( |B| = 25 \) (hockey)
- \( |C| = 20 \) (cricket)
- \( |A \cap B| = 10 \)
- \( |A \cap C| = 5 \)
- \( |B \cap C| = 8 \)
- \( |A \cap B \cap C| = 3 \)
Week 2: Lines and Distance
This week, we covered various geometric concepts related to lines and distances.
Important Concepts:
- Midpoint Formula: The midpoint of a line segment with endpoints \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is: \[ \left( \frac{x_1 + x_2}{2}, \frac{y_1 + y_2}{2} \right) \]
- Distance Formula: The distance between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) is: \[ \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
- Equation of a Line: The general form is \(Ax + By + C = 0\).
- Distance Between Two Parallel Lines: The distance between \(Ax + By + C_1 = 0\) and \(Ax + By + C_2 = 0\) is: \[ \frac{|C_2 - C_1|}{\sqrt{A^2 + B^2}} \]
- Sum of Squared Errors: A measure used in regression analysis to determine the accuracy of a model.
Week 3: Quadratic Functions
We delved into quadratic functions, their properties, and their graphs.
Important Concepts:
- Quadratic Function: A function of the form \(f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c\).
- Vertex: The highest or lowest point on the graph of a parabola, given by: \[ \left( -\frac{b}{2a}, f\left( -\frac{b}{2a} \right) \right) \]
- Discriminant: Determines the nature of the roots of a quadratic equation \(ax^2 + bx + c = 0\), given by: \[ \Delta = b^2 - 4ac \]
Week 4: Polynomials
This week, we explored polynomials and their properties.
Important Concepts:
- Zeros of a Polynomial: The values of \(x\) for which \(P(x) = 0\).
- Factors of a Polynomial: Expressions that can be multiplied to get the polynomial.
- Intercepts: Points where the graph intersects the axes.
- Multiplicity of Roots: The number of times a particular root appears.
- End Behavior: The behavior of the graph as \(x\) approaches \(\pm \infty\).
- Turning Points: Points where the graph changes direction.
Mid-Term Focus (Weeks 5 to 8)
For the mid-term quiz, more weightage will be given to topics from weeks 5 to 8, but questions from weeks 1 to 4 will also be included.
Week 5: Functions
We studied different types of functions and their compositions.
Important Concepts:
- One-to-One Function: A function where each element of the range is mapped to by exactly one element of the domain.
- Onto Function: A function where every element of the range is mapped to by at least one element of the domain.
- Composition of Functions: Combining two functions \(f\) and \(g\) to form \(f(g(x))\).
Week 6: Logarithmic Functions
This week, we focused on logarithmic functions and their properties.
Important Concepts:
- Logarithmic Function: The inverse of an exponential function, given by \(y = \log_b(x)\).
- Properties of Logarithms: \[ \log_b(xy) = \log_b(x) + \log_b(y) \] \[ \log_b\left(\frac{x}{y}\right) = \log_b(x) - \log_b(y) \] \[ \log_b(x^y) = y \log_b(x) \]
- Concept of Limits: Understanding the behavior of functions as they approach specific points.
- L'Hôpital's Rule: A method to evaluate limits of indeterminate forms: \[ \lim_{x \to c} \frac{f(x)}{g(x)} = \lim_{x \to c} \frac{f'(x)}{g'(x)} \]
Week 8: Continuity and Differentiability
In Week 8, we focused on the concepts of continuity and differentiability, which are fundamental in calculus.
Continuity:
A function \( f(x) \) is continuous at a point \( x = a \) if the following three conditions are met:- \( f(a) \) is defined.
- \( \lim_{x \to a} f(x) \) exists.
- \( \lim_{x \to a} f(x) = f(a) \).
Differentiability: A function \( f(x) \) is differentiable at a point \( x = a \) if the derivative \( f'(a) \) exists. This implies that the function is smooth and has no sharp corners or cusps at \( x = a \).
Equation of Tangent and Linear Approximation
Equation of Tangent: The equation of the tangent line to the curve \( y = f(x) \) at the point \( (a, f(a)) \) is given by: \[ y - f(a) = f'(a)(x - a) \] This line touches the curve at exactly one point and has the same slope as the curve at that point.
Linear Approximation: Linear approximation is used to approximate the value of a function near a given point. The linear approximation of \( f(x) \) near \( x = a \) is: \[ f(x) \approx f(a) + f'(a)(x - a) \] This is essentially the equation of the tangent line and provides a good approximation for values of \( x \) close to \( a \).
End-Term Focus: Graph Theory
Question will be from week 1 to 11
For the end-term exam, more weightage will be given to graph theory. Here are the key topics:
Week 9: Integration
Integration: Integration is the process of finding the integral of a function, which represents the area under the curve of the function. The definite integral of \( f(x) \) from \( a \) to \( b \) is given by: \[ \int_a^b f(x) \, dx \]
Riemann Sum: The Riemann sum is a method for approximating the definite integral of a function. It involves dividing the interval \([a, b]\) into smaller subintervals and summing up the areas of rectangles formed by the function values at specific points within the subintervals.
Graph Theory
Breadth-First Search (BFS) and Depth-First Search (DFS): BFS and DFS are fundamental algorithms for traversing graphs. BFS explores all neighbors of a vertex before moving on to the next level, while DFS explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG): A DAG is a directed graph with no cycles. It is important for representing tasks with dependencies.
Topological Sorting: Topological sorting is used to order the vertices of a DAG such that for every directed edge \( uv \), vertex \( u \) comes before \( v \). This is crucial for scheduling tasks.
Longest Path in DAG: Finding the longest path in a DAG is important for determining the maximum time required to complete a sequence of tasks.
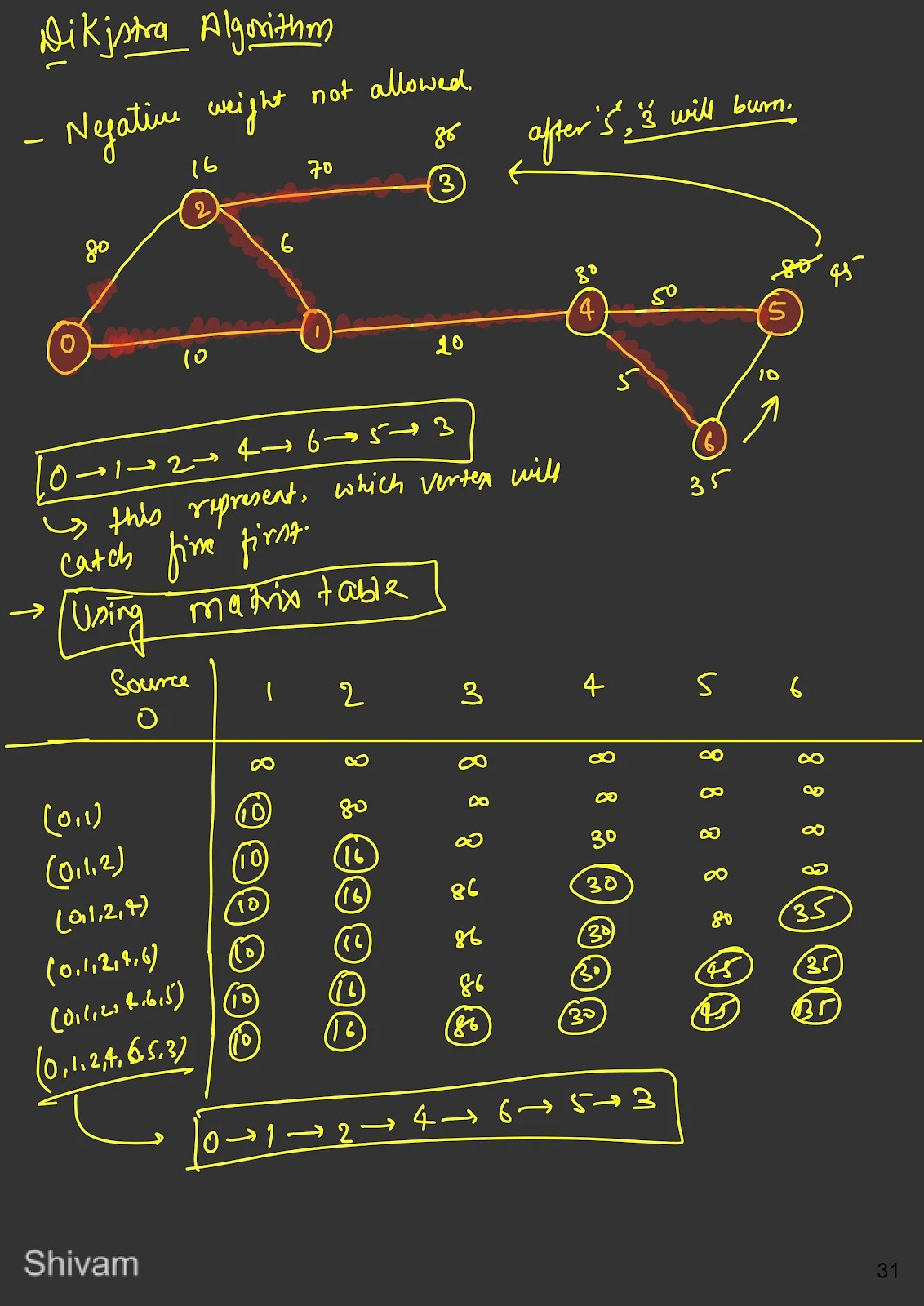
Dijkstra's Algorithm: Dijkstra's algorithm finds the shortest path from a source vertex to all other vertices in a graph with non-negative weights. It does not work with negative weights.
Bellman-Ford and Floyd-Warshall Algorithms: These algorithms handle graphs with negative weights but no negative cycles. Bellman-Ford works by iterating over all edges, while Floyd-Warshall considers all pairs of vertices.
Minimum Cost Spanning Tree (MCST): An MCST connects all vertices in a graph with the minimum total edge weight. Kruskal's and Prim's algorithms are used to find the MCST.
Kruskal's Algorithm: Kruskal's algorithm sorts all edges and adds them one by one to the spanning tree, ensuring no cycles are formed.
Prim's Algorithm: Prim's algorithm starts with a single vertex and grows the spanning tree by adding the smallest edge that connects a vertex in the tree to a vertex outside the tree.
Both algorithms yield the same MCST, and it's useful to cross-verify the results obtained from one algorithm with the other.
For quick revision check out short notes on youtube
Best of luck for your exams!